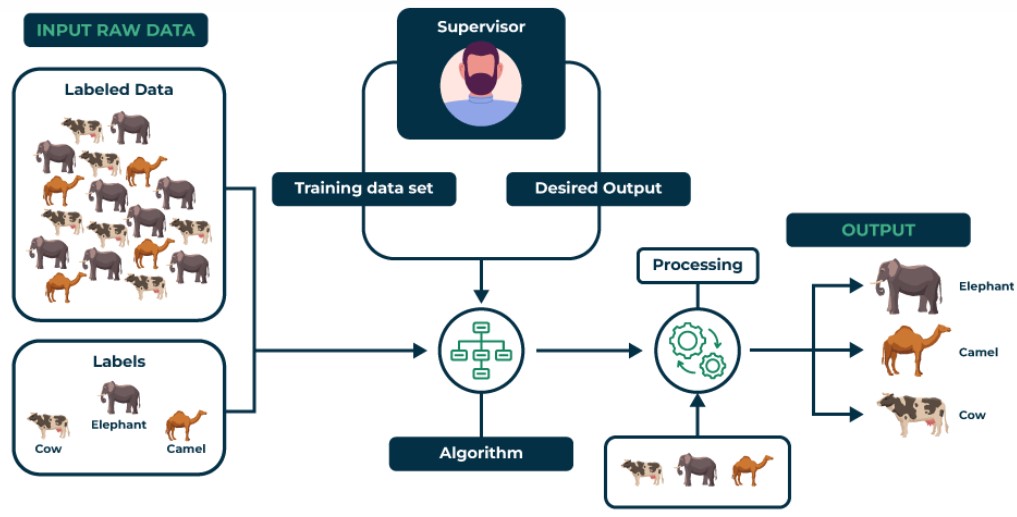
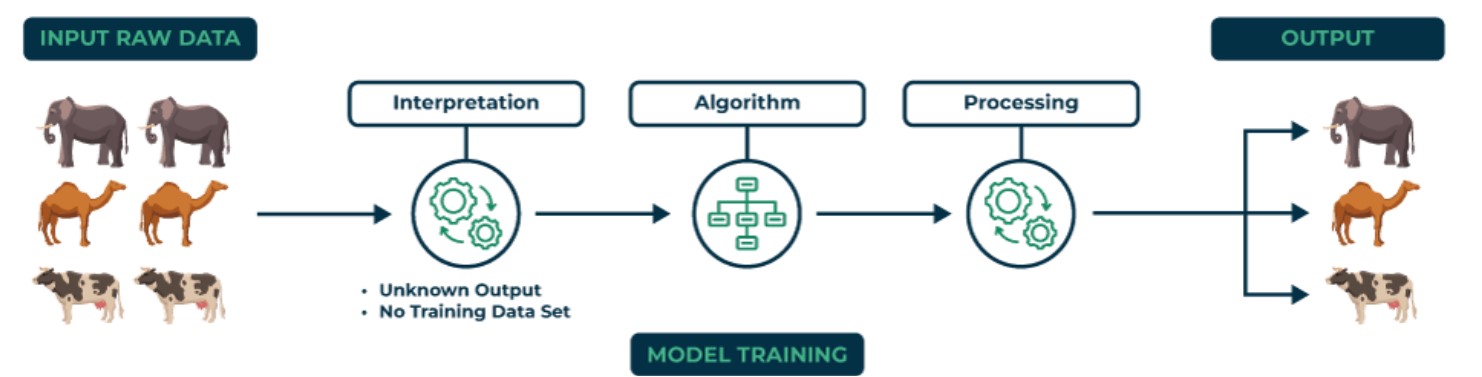
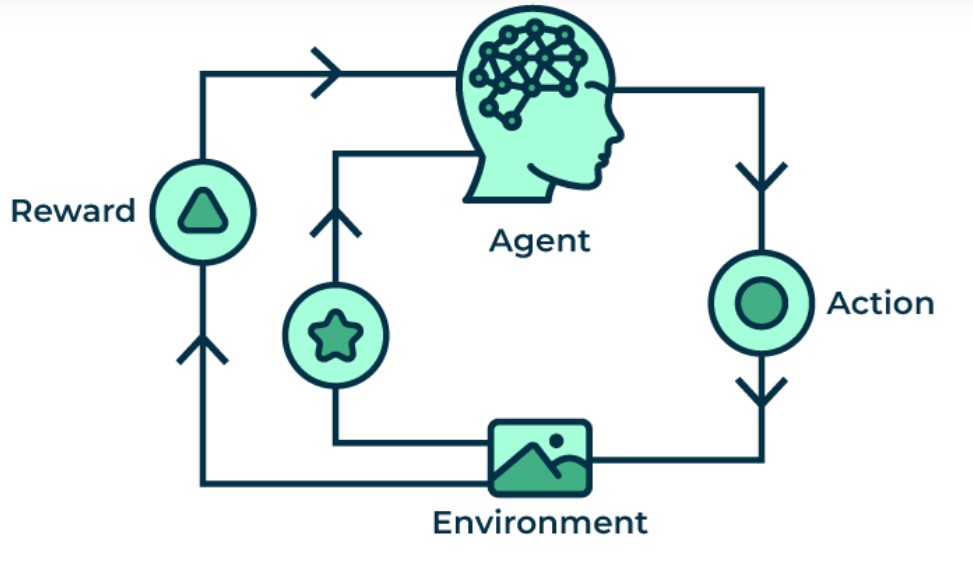
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is like a teacher guiding the machine. The model learns from labeled data, where both the input (features) and the correct output (labels) are provided. The goal is to predict the output for new data.
How it works: The model studies the examples during training and tries to generalize this learning to make predictions on unseen data.
Examples:
- Predicting House Prices: Using data like size, location, and number of rooms to estimate house prices.
- Spam Email Detection: Classifying emails as spam or not spam based on their content.