What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a technology that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. By analyzing patterns and examples, ML systems become smarter over time.
Examples: Email spam detection, movie recommendations, and self-driving cars.
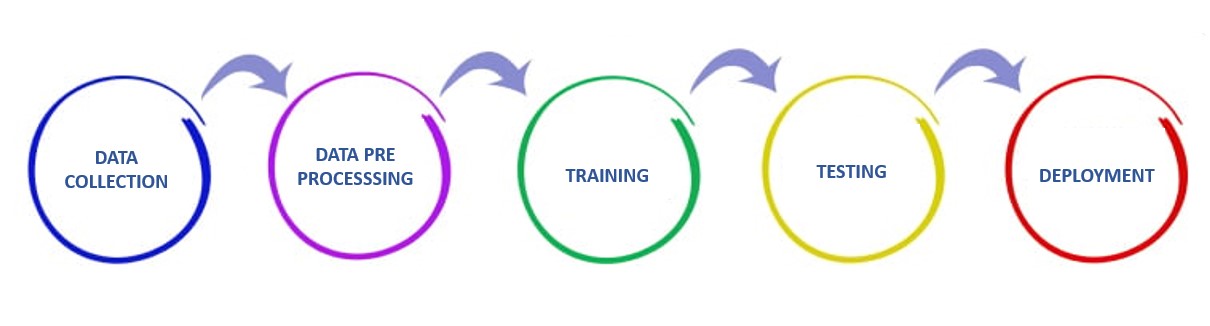
Step 1: Data Collection
Data collection is the first step in any machine learning project. It involves gathering relevant data from various sources, such as sensors, websites, or databases. The quality and quantity of the data play a vital role in the success of the ML model.
Example: Collecting images of animals to build a model that can identify different species.
Step 2: Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is about cleaning and organizing the data to make it suitable for training the model. This step involves removing duplicate entries, handling missing data, and transforming the data into a consistent format.
Example: Converting handwritten text into digital format for a handwriting recognition model.
Step 3: Model Training
In this step, the ML model is trained on the prepared data. The training process involves feeding the data into the model and adjusting its parameters so it learns to make accurate predictions.
Example: Training a model to recognize cats and dogs using thousands of labeled images.
Step 4: Model Testing
After training, the model is tested on new, unseen data to evaluate its accuracy. This helps ensure that the model performs well in real-world scenarios.
Example: Testing a spam email detector with new emails it hasn't seen before.
Step 5: Deployment
Once the model is tested and performs well, it is deployed to be used in real-world applications. Deployment involves integrating the model into software or systems where users can benefit from its predictions.
Example: Deploying a voice assistant like Siri to smartphones for everyday use.